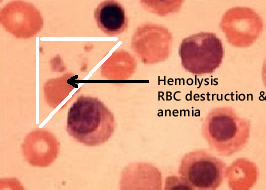
Hemolysis often presents with chronic or acute anemia, jaundice, or radiculopathy. Hemolytic anemia is usually caused by an elevated serum albumin concentration. The diagnosis of hemolytic anemia is based on elevated haptoglobin, elevated unconjugated bile, jaundice, and decreased hemoglobin S-100 in the blood. In patients with jaundice, elevated bilirubin, elevated serum albumin, or low hemoglobin may cause hemolytic anemia. In patients with radiculopathy, decreased levels of both soluble and insoluble collagens can cause this condition.
Hemolytic anemia can result from the presence of leukotriene-conjugated enzyme hemolytic enzymes (LTCE) in the bloodstream. When an increase in LTCE production occurs, it can lead to increased heme excretion, which leads to an increase in serum albumin concentration and an increase in circulating ferritin levels. Elevated serum albumin and high circulating ferritin levels can also contribute to hemolytic anemia.
Normal hemoglobin levels can vary widely from person to person. Therefore, it is very difficult to determine the appropriate hemoglobin level in patients with hemolytic anemia, especially in patients with normal serum albumin concentration. It is generally recommended that serum albumin levels be measured using Doppler ultrasound in patients with hemolytic anemia.
In addition to measuring albumin levels, Doppler ultrasound can also be used to measure blood pressure and cardiac output. Measurements of these variables can help diagnose hemolytic anemia and treat hemolytic anemia. Results are usually expressed as means or medians. The most accurate hemolytic anemia values usually depend on the total hemoglobin units and the percentage of hemoglobin present in the red blood cells.

Hemoglobin is the main protein found in red blood cells. Hemoglobin is separated from the plasma and transported to other organs when blood is pumped out. There are several types of hemoglobin.
Patients suffering from hemolytic anemia can be diagnosed based on the type of hemoglobin present in their blood, known as the type of hemoglobin. There are four types of hemoglobin: A, B, AB, O, G2, and T. A, B, O, and G2 are four different types of hemoglobin. Blood cells can have any of these four types of hemoglobin in their membrane, but the most common types are usually A, B, O, G2, and T. Each type of hemoglobin differs in its health effects and properties.
Because hemoglobin is the substance responsible for transporting oxygen to tissues, in the absence of hemoglobin, the blood cannot carry oxygen and other nutrients to other parts of the body. Anemia develops due to anemia. Red blood cells carry less oxygen to other parts of the body, causing an increased risk of infection, anemia, or even anemia due to reduced blood supply to the brain. Anemia can damage organs, such as the brain or heart, when the blood supply is insufficient to allow enough oxygen to pass through the blood vessels, damaging the cellular structure and increasing the risk of death.
In patients with hemolysis, measuring albumin and hemoglobin levels can be helpful in diagnosing hemolytic anemia and determining the need for treatment to increase levels of these substances. Doppler ultrasound results are used to diagnose and treat hemolytic anemia. The test results will help in the diagnosis of hemolytic anemia and the treatment of hemolytic anemia when the patient is anemic due to hemoglobin deficiency and there is an increased risk of infection, anemia due to increased blood supply to the brain, or when there is an increased risk of a blood clot in the brain.